Developed tools
Info
Enjoy summer, we'll be back in autumn. 
Logistics Audit Tool
The logistics audit tool (LAT), conceived under the umbrella of the CASTLE (Interreg IV) project, analyses logistics and material management processes in manufacturing SMEs. These are internal and supply chain processes and procedures related to core logistics activities as order processing, inventory management, warehousing, packaging, transportation, etc. The underlying model for the CASTLE logistics audit tool is the Global Materials Management Operations Guide / Logistics Evaluation (MMOG/LE) methodology (ODETTE 2011). MMOG/LE is an assessment tool that enables an organization to conduct a comprehensive evaluation of its materials management and logistics capability and performance. A spreadsheet file has to be filled in by the evaluator and based on this input, the programme automatically generates results and other outputs that help the evaluator and the people involved in the assessment process to comprehend the results and set out improvement plans.
The difference in approaches between MMOG/LE and CASTLE is that CASTLE is focused on defining and rounding up relevant logistics criteria applicable to SMEs in order to get a clear overview of their strengths and weaknesses. MMOG/LE, on the other hand, is not customized to SMEs. An important difference is also the aim of the two methodologies. While MMOG/LE is meant as a self-assessment or audit tool, CASTLE's main aim is to analyse logistics problems on the industry level. This information is to be used for policy-making purposes.
The CASTLE tool can clearly also be used for self-assessment, but it will not grade the company as A, B, or C supplier. Hence, the company will not get the same type of feedback as it would by using MMOG/LE.
The difference in approaches between MMOG/LE and CASTLE is that CASTLE is focused on defining and rounding up relevant logistics criteria applicable to SMEs in order to get a clear overview of their strengths and weaknesses. MMOG/LE, on the other hand, is not customized to SMEs. An important difference is also the aim of the two methodologies. While MMOG/LE is meant as a self-assessment or audit tool, CASTLE's main aim is to analyse logistics problems on the industry level. This information is to be used for policy-making purposes.
The CASTLE tool can clearly also be used for self-assessment, but it will not grade the company as A, B, or C supplier. Hence, the company will not get the same type of feedback as it would by using MMOG/LE.
The main logistics topics encompassed by the tool are:
- Logistics strategy and improvement,
- Supply chain,
- Work force organisation,
- Information systems,
- Procurement process analysis,
- Production process analysis, and
- Distribution process analysis.
There are around 8 criteria/standards for each logistics topic. Each criterion is named and briefly described. The LAT gives a range of choices to allow capturing the extent of compliance, which is useful when analysing a larger number of filled-out questionnaires:
- very bad: standard is not present, not implemented, not in place
- bad: standard isjust partially implemented, but not working properly
- average: standard is implemented and working properly, however further improvements are advisable
- good: standard is implemented and working well with some possible improvements
- world class: standard is implemented and working perfectly
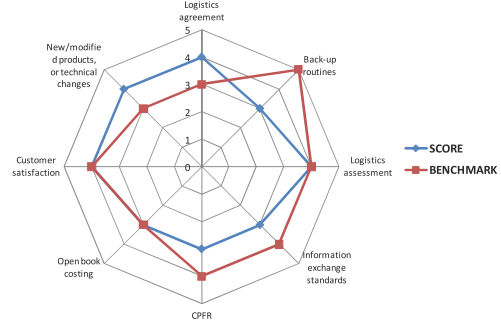
The LAT additionally uses different weights ranging from 1 to 3 to assess the level of importance of a single criteria/standard. The weights have been determined by a panel of external experts from CASTLE regions. In a further step, the weights have been used to define benchmarks for the interpretation of results. Based on that, a gap between expected performance (benchmark) and real performance (score) can be identified which is the basis for defining priority fields where policy intervention is needed. In the figure below, the results of a gap analysis for the supply chain topic are graphically displayed.